Thank You
Our team will get in touch with you shortly.
Why AAC Blocks Are the Smart Standard in 2025
In 2025, Autoclaved Aerated Concrete (AAC) blocks have evolved from a niche alternative into the smart standard for modern construction. Around the world – and notably across India – architects, engineers, and developers are rapidly shifting from traditional red clay bricks to AAC blocks. The reasons are clear: AAC blocks are lighter, faster to build with, and greener than conventional bricks. Today, many AAC block manufacturers in India, including Magicrete AAC Blocks, supply directly to projects, making availability easier than ever. A decade ago, AAC was considered a premium choice, but today the situation has reversed – red bricks are now roughly 20% more expensive than AAC in many regions. The push for high-rise structures and sustainable building practices drives this dramatic industry shift. If you are still asking whether AAC is right for your project, you might already be behind the curve — especially as explained in our blog on why AAC blocks are the top choice for modern builders. Many project tenders now explicitly specify AAC, underscoring its acceptance as the new normal in 2025.
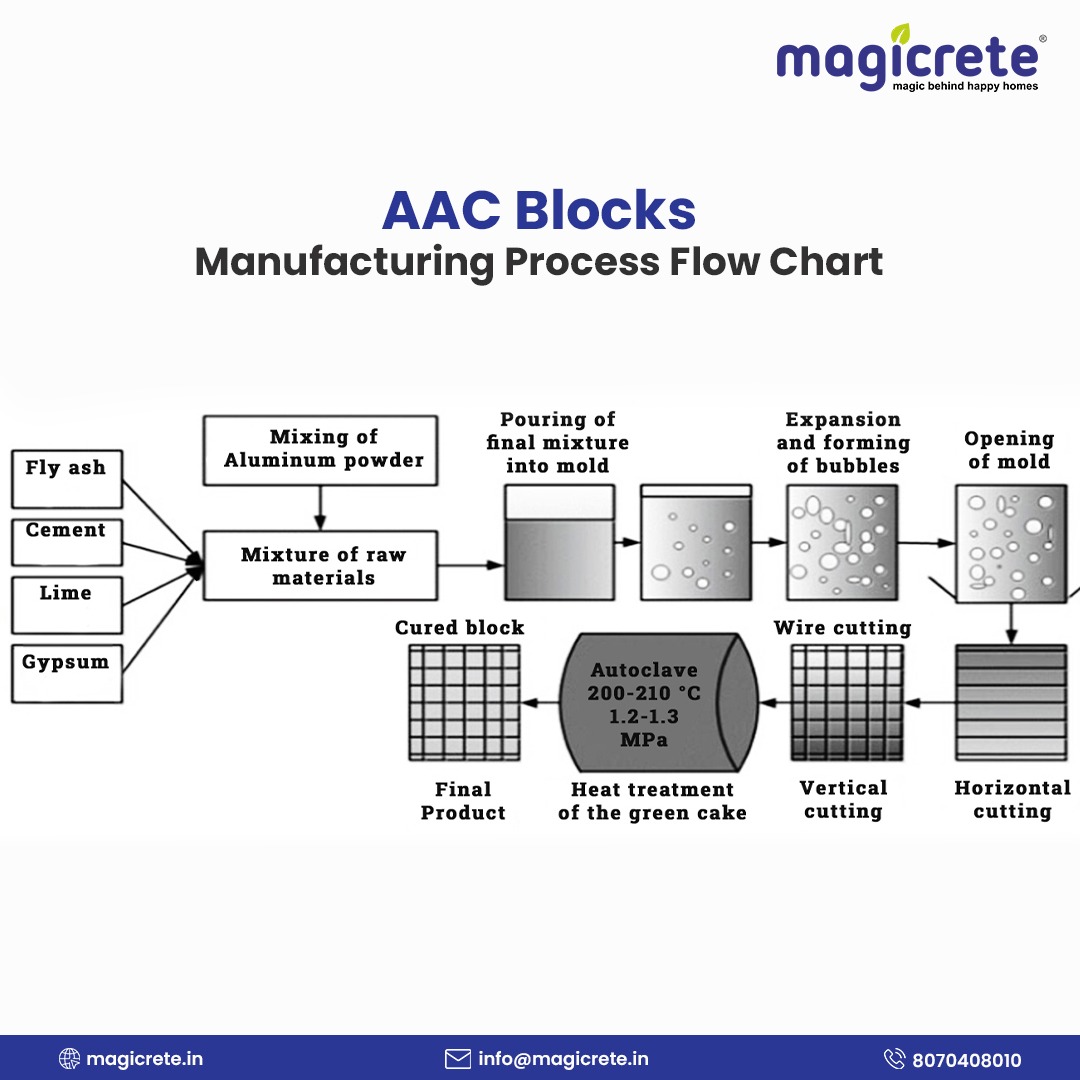
How AAC Blocks Are Manufactured?
AAC blocks are made through a precise process that combines raw materials like fly ash, cement, lime, and gypsum, followed by autoclaving and cutting into required sizes. The flow chart below shows the step-by-step AAC block manufacturing process:
Why Builders Prefer AAC Blocks Over Conventional Bricks?
What makes AAC blocks so popular among builders and contractors today? Below are key reasons construction professionals are replacing traditional red bricks with AAC blocks:
- Faster Construction: A typical AAC block (~ 600 mm long) can cover an area equivalent to 8–12 standard bricks. For example, building a 9 m² wall might require only ~65 AAC blocks versus 500+ bricks, drastically reducing the number of joints. Fewer joints and larger units translate to masonry work that is 4 times faster than bricklaying. Projects finish quicker, saving significant labor time and costs.
- Precise Dimensions (Less Plaster Work): AAC blocks are factory-molded with tight tolerances (often within ±3 mm). Their precision and smooth finish result in straighter walls by default. Unlike irregular bricks, AAC blocks stack evenly, so plaster thickness can be minimal for a smooth finish.
- Lighter Weight, Lower Structural Load: AAC is an ultra-lightweight concrete ~ 550–650 kg/m³ density, compared to 1,800+ kg/m³ for traditional bricks. Using AAC significantly reduces the dead load on the building. Lighter walls require smaller foundations and less reinforcing steel, yielding structural cost savings of up to 15% less steel and 7% less concrete.
- Thermal & Acoustic Insulation: Due to the presence of millions of air pores, AAC blocks offer excellent insulation against heat and sound. Buildings made with AAC walls are notably cooler in summer and warmer in winter. An AAC masonry wall can keep interiors about 5°C cooler in hot weather, reducing air-conditioning energy usage by up to 30%. This translates to big savings on HVAC bills and more comfortable rooms. Acoustically, AAC’s air pockets dampen sound transmission; a 100 mm thick AAC wall can achieve an STC (Sound Transmission Class) of ~43 dB or more, substantially higher sound reduction than a standard brick wall.
- Eco-Friendly & Sustainable: AAC blocks are often called a “green building material.” They incorporate fly ash (a waste byproduct from power plants) as a major ingredient, recycling this material instead of consuming new soil. In contrast, red brick production depletes valuable topsoil and requires energy-intensive kiln firing. The AAC manufacturing process emits far less CO₂ and uses no clay or coal fuel, making it much kinder to the environment. The blocks are also non-toxic and chemically inert. Using AAC can contribute to green building certifications such as LEED or IGBC points, as explained in environmental benefits of using fly ash in AAC blocks.
- Fire Resistance: AAC is non-combustible. It can endure high temperatures without structural failure. A 4-inch AAC wall provides about 4 hours of fire resistance, which is significantly higher than a typical brick wall. This makes AAC compliant with fire safety norms for walling material (it’s rated as Fire Rating Class A per IS and international standards). Many hospitals, hotels, and industrial buildings choose AAC for fire-rated partition walls for this reason.
- Water Absorption: AAC’s closed cellular structure gives it a moderate water absorption. As per IS 2185, the water absorption of AAC blocks should be ≤ 10% by mass after 24-hour immersion. In practice, good AAC blocks have absorption around 5–10%. By comparison, clay bricks often absorb 15–20% of their weight in water, which can lead to issues like efflorescence and dampness. AAC’s lower absorption means it’s less prone to seepage and salt deposits.
- Termite/Pest Resistance: Unlike wood, AAC is immune to termites and pests, it’s inorganic and solid. Also, AAC doesn’t harbor fungi or mold easily because of its mineral composition and the fact it doesn’t retain excessive moisture. This makes it suitable in tropical climates where termites or mold can be a problem in walls.
AAC Block Sizes & IS Standards Explained
One of the practical questions for architects and site engineers is: What sizes do AAC blocks come in, and how do they fit into building plans? AAC blocks are produced in a range of standardized sizes specified byIS 2185 (Part 3)that make modular construction straightforward. The majority of AAC blocks on the market are 600 mm x 200 mm face size with varying thicknesses include 100 mm, 150 mm, 200 mm, and sometimes 250 mm or 75 mm for special uses.
(Explore Magicrete AAC Block Technical Data Sheet)
AAC Block Sizes & When to Use Them.
It depends on the application and design requirements. Generally:
- 100 mm thick blocks (4″) – Used for interior partition walls or infill masonry that isn’t load-bearing. They are lightweight and maximize floor space usage.
- 150 mm thick blocks (6″) – Often used for exterior infill walls in high-rise frames or for single-story external walls where loads are moderate. Provides extra insulation over 100 mm.
- 200 mm thick blocks (8″) – Common for external load-bearing walls in low-rise construction (G+1 or G+2 buildings). Also used for high-rise shaft walls or fire walls where sturdiness is needed.
- 250 mm thick blocks (10″) – Ideal for taller structures or heavy-duty walls, where additional thickness adds strength and thermal mass. Used in some high-rise infill scenarios to achieve faster masonry (thicker block means fewer courses per floor).
IS Code for AAC Blocks – IS 2185 (Part 3): 1984
Specifically, covering autoclaved cellular concrete blocks is non-negotiable for structural safety. This standard outlines not just sizes but also physical requirements like minimum compressive strength, drying shrinkage limits, density categories, water absorption, etc.
Strength & Durability – What is the Compressive Strength of AAC Blocks?
Compressive strength is the metric that defines how much load a material can bear per unit area before crushing. AAC blocks, despite being lightweight, have respectable compressive strength in the range of 3.5 to 5 N/mm². According to IS 2185 (Part 3), AAC blocks must have a minimum compressive strength of 3 N/mm² to be used in masonry construction.
AAC Block Density & Weight vs Strength: It’s important to understand that AAC blocks achieve their strength at a much lower weight compared to traditional materials. Typical dry density of AAC is 550–650 kg/m³, which is almost 3 times lighter than concrete or brick masonry (brick density ~ 1600–1900 kg/m³). This low density is due to the air voids, but the autoclaving process gives the material a robust crystalline structure that can carry loads well. In practical terms, a single 8-inch AAC block weighs ~15 kg, yet that block can support load in a wall that would require 8–10 bricks (which together weigh ~30+ kg). The strength-to-weight ratio of AAC is therefore very high.
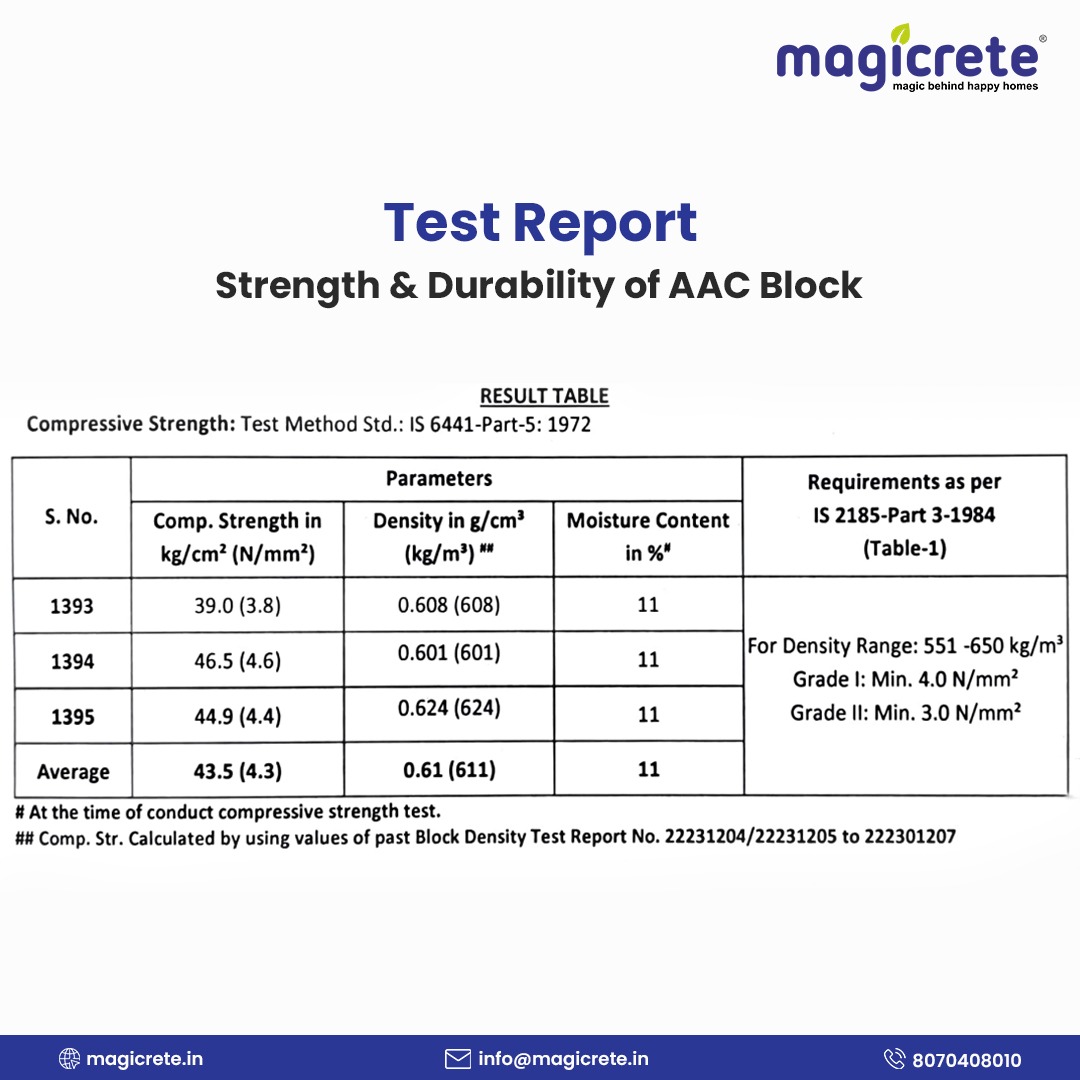
To explore this in detail, check out our full guide on the Compressive Strength of AAC Blocks.
AAC Blocks vs Red Bricks – Which is Better?
It’s a common question on construction sites: AAC blocks vs. red bricks – which should we use? Both have been used to build homes, apartments, and offices, but they differ in almost every aspect. Here we compare AAC blocks and conventional burnt clay bricks across key parameters:
Factor | AAC Blocks | Red Clay Bricks |
Unit Size | Large:Typical block size is 600×200×100 mm (1 AAC block ≈ 9 bricks). | Small:Typical brick size is 230×115×75 mm. |
Weight & Density | Lightweight:~550–650 kg/m³ density | Heavy:~1600–1800 kg/m³ density. |
Thermal Insulation | High: Thermal conductivity ~0.2 W/m·K. Excellent insulator – walls stay cooler, can cut AC costs ~30% | Low: Thermal conductivity ~0.6 W/m·K. Poor insulator – walls easily transmit heat, making interiors warmer. |
Sound Insulation | Good sound absorption(STC ~45 for 200mm wall). The air voids dampen noise, providing quieter interiors. | Moderate sound insulation(STC ~30 for 230mm wall). Heavier but solid, transmits sound unless the wall is thick or cavity provided. |
Construction Speed | Fast build: Large blocks mean a mason can lay ≈1 AAC block in the time of ~10 bricks. Fewer joints (less mortar mixing). Overall construction can be ~20–30% faster. | Slower build: Small bricks take longer to lay – more than 8–10× the number of units and joints. More time spent on aligning and leveling each course. Higher mortar consumption and frequent rehandling of bricks. |
Material Wastage | Minimal wastage (factory-made blocks have <2% breakage typically). Precise dimensions mean almost no on-site adjustment. | Higher wastage (5–10% breakage is common during transport/handling). Non-uniform bricks often require chipping to fit, generating waste. |
Environmental Impact | Eco-friendly: Made from industrial waste (fly ash), less energy in production. No clay mining or coal firing. Lower carbon footprint and qualifies for green building credits. AAC is recyclable and produces less site pollution. | Environmentally taxing: Requires mining of fertile clay (topsoil depletion) and burning fuel (coal/wood) for kilns, releasing CO₂ and pollutants. Brick production contributes to air pollution and land degradation. Used bricks often end up as debris. |
Looking at the comparison, it’s evident why AAC blocks are often considered the smarter choice today. They are lighter, larger, and packed with performance benefits (insulation, fire resistance, etc.) that contemporary buildings demand. Red bricks, on the other hand, used for centuries and are known for their durability and high compressive strength in certain grades. However, bricks come with hidden costs: the need for more material and labor, and lower thermal efficiency.
Still comparing AAC Blocks vs red bricks? Don’t miss our in-depth analysis on the AAC Blocks vs Red Bricks Cost & Use Cases.
AAC Block Price & Availability in 2025
With all their advantages, one might wonder: How much do AAC blocks cost, and can I get them easily? The good news is that AAC blocks are not only more affordable than before, but also widely available across regions.
AAC block price in India: ₹3,500–₹4,000/m³. This is quite competitive when you consider one cubic meter of AAC can cover about 8–10 m² of wall area (depending on thickness). Importantly, the gap between AAC and brick costs has closed. Clay bricks, once much cheaper, have risen in price due to high fuel and labor costs. Now, AAC blocks often cost the same or even less than an equivalent volume of bricks. And when you factor in the overall construction cost, AAC usually saves money by reducing ancillary material and labor.
If you search for ‘AAC blocks near me,’ you can quickly Find an AAC Dealer Near You through our dealer locator. you’ll find over 200+ AAC block plants across India (in Gujarat, Maharashtra, Tamil Nadu, West Bengal, and more). Many leading AAC block manufacturers like Magicrete supply nationwide. This means wherever your project is, chances are there’s an AAC block manufacturer or dealer relatively nearby. Builders can source AAC blocks through local building material suppliers or directly from manufacturers’ sales offices. Many large brands have dealer networks in every major city.

AAC Is No Longer a Premium Choice, It’s the Smart One
As we’ve explored, AAC block have proven themselves on all fronts, from structural adequacy and speed of construction to thermal comfort and sustainability. In 2025, using AAC is no longer about being fancy or experimental; it’s about being smart and efficient. These lightweight blocks have achieved near parity with brick costs, while offering far superior performance in key areas like weight reduction, insulation, and workability. For architects and builders, AAC opens up possibilities for taller structures and innovative designs due to its light weight and large format, all while meeting the demands of energy-efficient green construction. Engineers appreciate that AAC comes with standardized quality (factory-made) and simplifies compliance with building norms (fire, sound, etc.). Contractors save time and labor, finishing projects faster with less waste to haul off-site.
In short, AAC blocks have transitioned from a “premium” alternative to the go-to solution for modern masonry. If you’re aiming to deliver projects that are on-time, on-budget, and high-performance, AAC is a material you can’t ignore. It embodies the construction industry’s move towards smarter, cleaner, and more cost-effective methods.
Finally, choosing the right AAC block supplier is crucial to fully reap the benefits. For example, Magicrete AAC Blocks are IS-certified and ISO 9001 compliant, with a wide range of sizes and nationwide dealer support.
In 2025 and beyond, AAC blocks aren’t just an alternative; they are the future of building, happening right now. It’s time to build lighter, faster, and smarter. Welcome to the AAC revolution in construction!
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1. What is the full form of AAC blocks?
AAC stands for Autoclaved Aerated Concrete. These blocks are lightweight, precast building materials made from fly ash, cement, lime, and gypsum.
Q2. Are AAC blocks better than red bricks?
Yes, AAC blocks are lighter, faster to build with, and provide superior thermal and sound insulation compared to red bricks. They also cost less overall due to reduced labor and material usage.
Q3. How much do AAC blocks cost in India in 2025?
AAC block prices in India average ₹3,500–₹4,000 per m³. This usually works out cheaper than red bricks when factoring labor, mortar, and plaster savings.
Q4. What is the lifespan of AAC blocks?
AAC blocks are highly durable with a lifespan of 70–100 years if installed correctly. They don’t warp, crack easily, or get damaged by termites.
Q5. Can AAC blocks be used for load-bearing walls?
Yes, AAC blocks are strong enough for low-rise load-bearing construction. For high-rises, they are typically used as infill or partition walls within RCC frames.
Q6. Do AAC blocks absorb water?
AAC blocks have a moderate water absorption of 5–10%, much lower than clay bricks (15–20%). Proper plastering prevents seepage or dampness issues.
Q7. Are AAC blocks eco-friendly?
Yes. AAC blocks recycle industrial waste (fly ash), save topsoil, reduce CO₂ emissions, and contribute to green building certifications like LEED or IGBC.
Q8. Where can I buy AAC blocks near me?
AAC blocks are available through local building material suppliers and dealers across India. Brands like Magicrete have nationwide dealer networks for easy availability.
Content
- Why AAC Blocks Are the Smart Standard in 2025
- How AAC Blocks Are Manufactured?
- Why Builders Prefer AAC Blocks Over Conventional Bricks?
- AAC Block Sizes & IS Standards Explained
- Strength & Durability – What is the Compressive Strength of AAC Blocks?
- AAC Blocks vs Red Bricks – Which is Better?
- AAC Block Price & Availability in 2025
- AAC Is No Longer a Premium Choice, It’s the Smart One
- Frequently Asked Questions



